Ischialgia is pain felt along the leg. Judging from the sense of the word, then ischialgia is pain felt along N.ischiadicus. So ischialgia defined as pain felt along the nerve and subsequent ischiadicus along the legs. Ischialgia is a condition where the nerves Ischiadicus, which innervate butt to foot pinched area, in that case, which is pinched nerves Ischiadicus right side. This can happen due to some disease processes such as physical trauma, chemical, and electrical, infections, metabolic problems, and autoimmune. Ischialgia increase in frequency along with the many activities undertaken.
Medical Health Information about Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment and Therapy of Disease also Healthy Tips
Showing posts with label Headache and Vertigo Neurology. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Headache and Vertigo Neurology. Show all posts
Treatment and Therapy of Cluster Headache
Medical Treatment and Therapy of the cluster headache can be divided into the treatment of acute attacks, and preventive medicine, which aims to suppress the attack. Acute and preventive treatment started simultaneously when the initial period of the cluster. Latest surgical treatment options and neuro stimulation has replaced detrimental treatment approaches.
Pathophysiology of Cluster Headache
The pathophysiology of cluster headache is still remains unclear. However, there are several theories regarding the pathophysiology of Cluster headache. One theory is that the focus of the pathophysiology of cluster headache is located in the carotid artery which stimulates intracavernous pericarotis plexus.
Medical Treatment and Therapy for Tension Headache
The principle of treatment is psychologic approach (psychotherapy), physiological (relaxation) and pharmacological (analgesic, sedative and minor transquilizers). In practice, it needs an adequate explanation of the background of the pain that the patient understands, about the issues that are less or not realized.
Clinical Manifestations of Tension Headache
The symptoms that can occur in tension headache are: a headache that felt like a heavy head, stiff as tied rope wrapped around head, and pressed tight. Sometimes with throbbing headache. If prolonged, on palpation can be found swollen, hard and tenderness area. Can also be accompanied by symptoms are: nausea, vomiting, vertigo, fatigue, difficulty to sleep, nightmares, frequent waking early in the morning and fall asleep, hyperventilation, abdominal bloating, sadly, the loss of the will to learn or work, anorexia and other depressive complaints. Pain can also be felt as a tense feeling the pinch in the head and pain located in the area occipitocervicale.
Pathophysiology of Tension Headache
Tension Headache pathophysiology is still not clearly known. In some of the literature and research results mentioned several circumstances relating to the occurrence of Tension Headache as follows:
(1) central nervous system dysfunction that is more involved than the peripheral nervous system dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system which leads to more ETTH, whereas central nervous system dysfunction leads to CTTH (Chronic Tension Type Headache) ,
(1) central nervous system dysfunction that is more involved than the peripheral nervous system dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system which leads to more ETTH, whereas central nervous system dysfunction leads to CTTH (Chronic Tension Type Headache) ,
Tension Headache
 Type Tension headache or tension-type headache is defined as a sensation of heaviness or pressure that settled, on both sides of the head arising episodic and associated with stress, but it can be repeated almost every day without any psychological factors. The pain arises due to continued contraction of the muscles of the head and neck is m. splenius capitis, m. temporalis, m.maseter, m. sternocleidomastoid, m. trapezius, m. posterior cervical, and m. levator scapula.
Type Tension headache or tension-type headache is defined as a sensation of heaviness or pressure that settled, on both sides of the head arising episodic and associated with stress, but it can be repeated almost every day without any psychological factors. The pain arises due to continued contraction of the muscles of the head and neck is m. splenius capitis, m. temporalis, m.maseter, m. sternocleidomastoid, m. trapezius, m. posterior cervical, and m. levator scapula.Medical Treatment and Therapy for Migraine
 |
| Treatment and Therapy Migraine |
Migraine Treatment Targets
Migraine treatment and therapy goals depends on length and intensity of pain, symptoms comorbidities, degree of disability and the start of treatment response and may also be found in other diseases such as epilepsy, anxiety, stroke, myocardial infarction. Because it must be wary of the medicine. When there are symptoms of nausea/vomiting, the medicine is given rectally, nasal, subcutaneous or intravenous.
Migraine treatment and therapy goals depends on length and intensity of pain, symptoms comorbidities, degree of disability and the start of treatment response and may also be found in other diseases such as epilepsy, anxiety, stroke, myocardial infarction. Because it must be wary of the medicine. When there are symptoms of nausea/vomiting, the medicine is given rectally, nasal, subcutaneous or intravenous.
Diagnosis of Migraine
A. Migraine without Aura
Previous term: Common migraine, hemicrania simplex.
Description:
Recurrent headache attacks with manifestation for 4-72 hours. Characteristics unilateral head pain, throbbing, moderate intensity or severe, worsen with routine physical activity and followed with nausea and photophobia and phonophobia or.
Previous term: Common migraine, hemicrania simplex.
Description:
Recurrent headache attacks with manifestation for 4-72 hours. Characteristics unilateral head pain, throbbing, moderate intensity or severe, worsen with routine physical activity and followed with nausea and photophobia and phonophobia or.
Pathophysiology of Migraine
Vascular Theory
Intracranial vasoconstriction in the outer cortex plays a role in the occurrence of migraine with aura. This opinion is reinforced by the presence of headache accompanied with the same heart rate. Blood vessels constrict primarily located in the brain due to activation of peripheral nociceptive nerve locals. This theory was initiated above observation that the extracranial veins that will undergo vasodilation palpable heartbeat. This vasodilation will stimulate people to experience headaches. In such conditions, vasoconstrictor drugs, such as ergotamine will reduce headaches, while vasodilators such as nitroglycerin will worsen headaches.
Migraine
.jpg) |
| Migraine |
According to the International Headache Society (IHS) migraine is a vascular headache with recurrent pain attacks that lasts 4-72 hours. The pain is usually one sided (unilateral), its throbbing, pain is moderate to severe intensity, aggravated by activity, and can be accompanied by nausea and or vomiting, photophobia and phonophobia.
Medical Treatment and Therapy of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
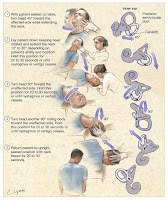
Management of BPPV include observation, medication to suppress vestibular function (vestibulosuppressan), canalith repositioning, and surgery. Primary election governance is observed, Because BPPV can own resolution in weekly or monthly. Therefore, most experts recommend that only observation. However, during the observation time of patients still suffer from vertigo. As a result, patients are faced with the possibility of falling when vertigo blaze while he was on the move.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of BPPV
Clinical Symptoms
BPPV occurs suddenly. Most patients are aware of the time they wake up, when to change position from lying to sitting. Patients feel dizzy spinning gradually diminished and disappeared. There is a lag between changes in head position with the onset of feeling dizzy spin. In general, feeling dizzy spinning arise very strong in the beginning and disappears after 30 seconds while its recurrent attacks become lighter. These symptoms are felt for days to months.
Pathophysiology of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
In the inner ear there are three semicircular canals. Three semicircular canals are located in areas that are mutually perpendicular to each other. At the base of each Semicircular canals, there is a widened portion which called ampula. In ampula there cupula, is a tool to detect the movement of fluid in semicircular canals as result of head movement. For example, when someone turned his head to the right, the fluid in the right canal semicircularis will be left, so Cupula will deflecting towards ampula. Deflection is translated in a signal goes to the brain so that the sensation arises head turned to the right. With the availability of particles or debris in Semicircular canals, will reduce or even create cupula deflection towards the head instead of the actual direction of motion. It gives a signal that is not in accordance with the direction of head movement, so that arise in the form of vertigo sensation.
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Vertigo is a complaint which often encountered in practice, is often described as a sense of spinning, feeling shaky, unstable (giddiness, unsteadiness), or dizziness; description of the complaint is important to know in order not to be confused with headache or cephalalgia, especially because among the laity, the second term (dizziness and headache) are often used interchangeably.
Medical Treatment and Therapy of Vertigo
Because the causes of vertigo are varied, while patients often feel very annoyed with vertigo symptoms, often using symptomatic treatment. The duration of treatment are varied. Most cases of therapy can be stopped after a few weeks and here are some commonly used classes of drugs:
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)