Clinical manifestations of Syringomyelia is highly variable depending on the direction of widening the syrinx, transverse or longitudinal direction. Widening usually occurs towards the anterior of the spinal canal rather than to the right or left. Syringomyelia usually takes place slowly. Course of the disease can be up to many years. Acute symptoms will appear when it is on the brain stem (like syringobulbi).
Medical Health Information about Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment and Therapy of Disease also Healthy Tips
Pathophysiology of Syringomyelia
Pathophysiology of syringomyelia is not widely known and most commonly used theory is the theory of Gardne , William and Oldfield .
Gardner's Hydrodinamic Theory
This theory suggests that syringomyelia is the result of a "water hammer" - like pulsatile transmission of Cerebrospinal Fluid ( SF) pressure, through a connection between the fourth ventricle and spinal canal centralis . Blockade originated from the foramen of Magendie.
This theory suggests that syringomyelia is the result of a "water hammer" - like pulsatile transmission of Cerebrospinal Fluid ( SF) pressure, through a connection between the fourth ventricle and spinal canal centralis . Blockade originated from the foramen of Magendie.
Classification of Syringomyelia
Classification of syringomyelia is still under debate, since the onset of the syrinx underlying pathogenesis is still under development and debate the experts.
Basically classification systems seen from:
Basically classification systems seen from:
Syringomyelia
What is Syringomyelia? for this session, it would be explained what Syringomyelia is. Syringomyelia is a chronic neurological syndrome that is pathologically found a syrinx in the spinal canal. Syringomyelia is a single lesion, tangible hole in the center of the central gray matter. Usually in the cervical or thoracic region. Syrinx can be connected with the central canal (canalis centralis) which called hidromyelia , or not related to the central canal, called syiringomyelia or be located in the central of the central canal called syringohidromelia. To facilitate the understanding of all the circumstances called syringomyelia .
Medical Treatment and Therapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
How to treat Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis? Here's explanation Medical Treatment and Therapy of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. No drug has been found to slow the progression of ALS. However, the Food and Drug Administration ( FDA ) has approved the first treatment for this disease is Riluzole. Riluzole is believed to reduce damage to motor neurons by decreasing the release of glutamate Clinical trials which performed to ALS patients, showed that administration of Riluzole can extend a patient's life until a couple of months, especially patients with difficulty swallowing.
Differential Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
There are several diseases that have symptoms and signs such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Here are some diseases that become differential diagnosis for, Amyotrophicl Lateral Sclerosis (ALS):
1. Another Motor Neuron Disease (MND)
a. Primary lateral sclerosis (UMN signs only)
b. Progressive muscular atrophy (LMN signs only)
c. Progressive bulbar palsy
1. Another Motor Neuron Disease (MND)
a. Primary lateral sclerosis (UMN signs only)
b. Progressive muscular atrophy (LMN signs only)
c. Progressive bulbar palsy
How to Make Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is difficult to be diagnosed since the beginning, because it may seem similar to some other neurological diseases. The medical experts caution after conducting a neurological examination tests to rule out other conditions, with signs of UMN and LMN in the same segment with asymmetrical anatomical localization is able to suspect the diagnosis of ALS. Examination that may be performed include:
Diagnostic Criterias for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
No test can provide a definite diagnosis of ALS, although the presence of interference at UMN and LMN in the body is very suggestive. The diagnosis of ALS is primarily based on signs and symptoms experienced by patients and through a series of investigations to rule out other diseases. Doctors dig deeply patient medical history and usually conduct a thorough neurological examination and to assess whether symptoms such as muscle weakness, atrophy of muscles, hyperreflexia, and spasticity worsened progressively. Because the symptoms of ALS can be similar to other illnesses, diseases that can be cured, appropriate tests should be performed to rule out other diseases.
Clinical Manifestations of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) symptoms are varies from one person to another according to the muscle groups that are affected by this disease. Tripping, dropping things, abnormal fatigue of the arms and / or legs, slurred speech, difficulty in speaking loud, uncontrollable laughing or crying, and muscle cramps and twitches all the symptoms of ALS. ALS usually starts first in the hand and will cause problems in dressing, bathing, or other simple tasks. It could develop into more on one side of the body and generally goes to the hands or feet. If start on foot, walking would be difficult. ALS can also start in the throat, causing difficulty swallowing. People with ALS do not lose their ability to see, hear, touch, smell, or taste. bladder and the muscles of the eye are not affected, nor desire and sexual function. The disease does not affect the mind of the patient.
Pathophysiology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
The precise molecular pathways leading to degeneration of motor neurons in ALS is not known , but as with other neurodegenerative diseases , is likely to be a complex interaction between the various cellular pathogenic mechanisms may not be mutually exclusive include :
Etiology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
The etiology is not known with certainly. ALS in 10% of cases derived autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive disorder which occurs on chromosome 2 or 21. Could be caused by a gene mutation for substances - toxic substances such as free radicals superoxide ions. Some are caused by an autoimmune process due to virus infection, especially poliovirus resulting in neuronal damage.
Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis
 |
| Lou Gehrig |
Amyotropic lateral sclerosis is often called Lou Gehrig's disease, Maladie de Charcot or motor neurone disease is a progressive fatal neurodegenerative disease caused by the degeneration of motor neurons.
Multiple Sclerosis Disease-Modifying Therapies
Therapy was given only to minimize the incidence of attack, reducing the effects of attacks, and prolong remission. Disease-modifying therapies for early management of MS is currently available in the United States: intramuscular interferon beta-1a (Avonex), subcutaneous interferon beta-1a (Rebif), interferon beta-1b (Betaseron), and glatiramer acetate (Copaxone). The fifth agent, mitoxantrone (Novantrone), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of relapsing-remitting MS and secondary progressive MS is deteriorating.
Treatment and Therapy for Relaps Multiple Sclerosis
What are treatment and therapy for relaps Multiple Sclerosis?
1 . Adrenal corticosteroids .
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy in reducing symptoms of acute relapses of MS. These agents work through immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects, restoration of blood brain barrier and reduces edema. corticosteroids can also improve axonal conduction. Corticosteroid therapy shortens the duration of acute relapse and accelerates recovery. However, corticosteroids have not been able to increase the overall recovery of MS.
Medical Symptomatic Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
Symptomatic therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
In addition to primary care, symptomatic therapy should also be considered such as:
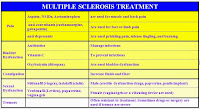 |
| Table Multiple Sclerosis Symptomatic Medicine |
In addition to primary care, symptomatic therapy should also be considered such as:
1. Spasticity
Mild spasticity can be reduced by stretching and exercise programs such as yoga, physical therapy, or other therapies. Medication administered when there are stiffness, spasm, or clonus on exertion or sleep state. Baclofen, Tizanidine, Gabapentin , and Benzodiazepines effective as antispasm agents.
Label:
Imuno Neurology
How to Make Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis
Diagnostic criteria commonly used is the McDonald’s criteria, which Multiple Sclerosis criteria with the original concept in 2001 and last revised in 2010. McDonald’s criteria emphasize the separation by time / disseminated in time two or more attacks) and separation by space / disseminated in space (two or more different diagnoses topis). Someone diagnosed definitely with Multiple Sclerosis when there is a separation of time and space that is clinically proven clinically or when evidence is incomplete but is supported by the investigation MRI, CSF or VEP).
Label:
Imuno Neurology
Clinical Manifestations of Multiple Sclerosis
What are Clinical Manifestations of Multiple Sclerosis?
Clinical Manifestations that appear according to the lesion area affected. There are several signs and symptoms that appear in multiple sclerosis:
a. Digestive and urinary dysfunction
b. The reduced perception of pain, vibration, and position
c. Fatigue and impaired mobility
d. Depression and cognitive or memory impairment
e. Vision and hearing problems
f. Tremor, hyperreflexia, spasticity, and positive Babinsky sign
g. Nystagmus, impaired coordination and balance.
Clinical Manifestations that appear according to the lesion area affected. There are several signs and symptoms that appear in multiple sclerosis:
a. Digestive and urinary dysfunction
b. The reduced perception of pain, vibration, and position
c. Fatigue and impaired mobility
d. Depression and cognitive or memory impairment
e. Vision and hearing problems
f. Tremor, hyperreflexia, spasticity, and positive Babinsky sign
g. Nystagmus, impaired coordination and balance.
Label:
Imuno Neurology
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
