The most common diagnostic tools used to investigate the effect is lymphangioma and ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound, computed tomography (CT scan) and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound shows hypoechogenic superficial multilocular cystic mass, but failed to show expansion retropharyngeal, axillary or mediastinum. With a CT scan, it may be difficult to distinguish the mass of soft tissue structures. More recently, MRI has been shown to be better in describing the boundaries of tumors and can more accurately describe the network.
Medical Health Treatment and Therapy
Medical Health Information about Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment and Therapy of Disease also Healthy Tips
Lymphangioma Signs and Symptoms
 |
| Lymphangioma |
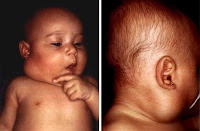
Lymphangioma Signs and symptoms vary according to the anatomical location. Two-thirds of cervical lymphangioma showed no symptoms. They are present as swelling multilobular, palpable cystic on palpation. Massa may have a limit but most often infiltrate. Posterior triangle of the neck and submandibular region was the most common being the location presentations.
Lymphangioma
 |
| Lymphangioma |
Definition
Lymphangioma is a collection of abnormal benign lymphatic vessels that form a mass that consists of cystic spaces with the size of the variance, which have the potential for local extension, so it can infiltrate surrounding structures. Lymphangioma, cystic hygroma, and limfangiomatosis can affect almost any area of the body where there is lymphatic tissue, but mostly in the head, neck and axilla.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)